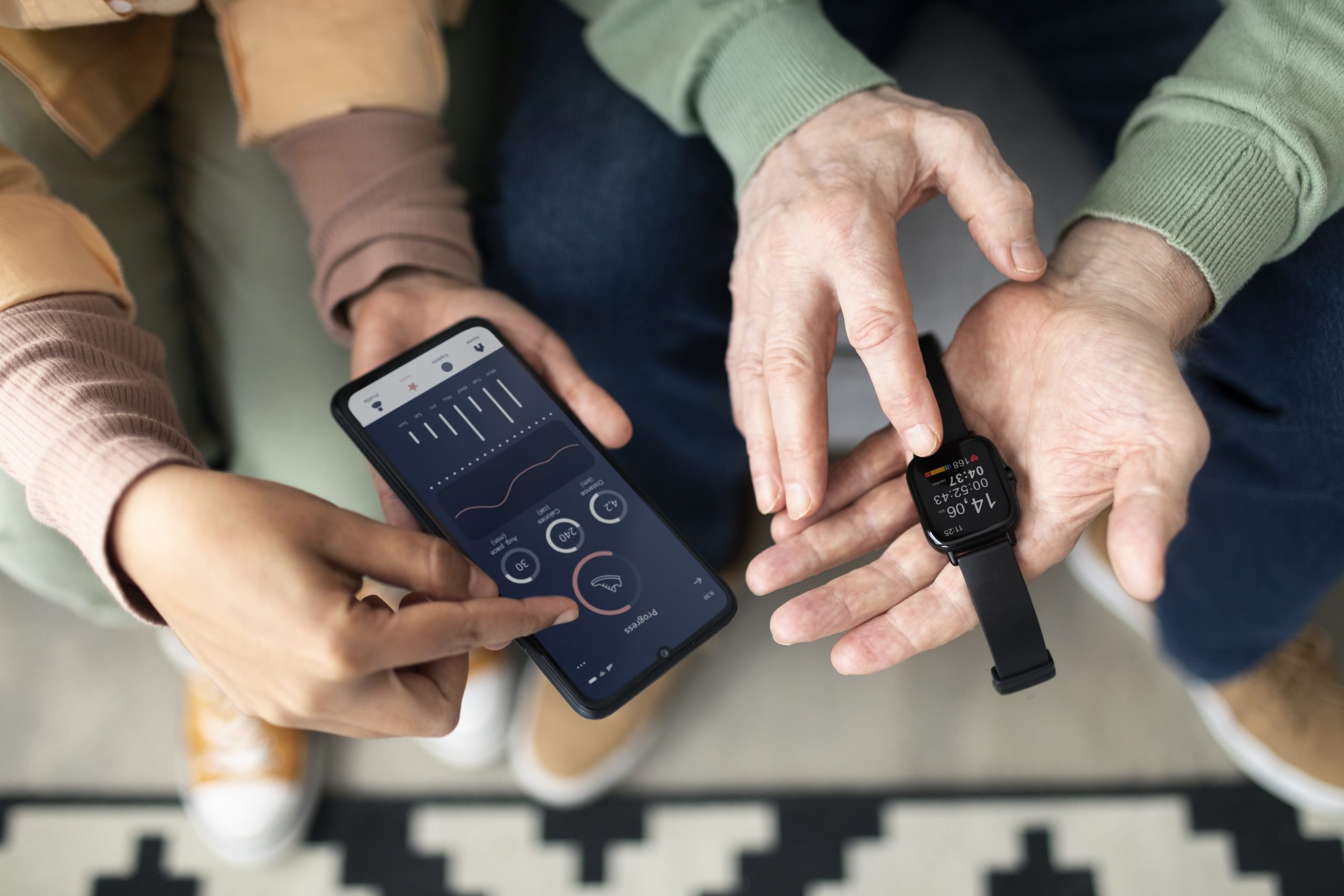
Separate from participating in physical activity, there are numerous harmful effects associated with prolonged sitting (e.g., increased risk of cancer, diabetes, and heart disease). With individuals, on average, being sedentary for nearly eight hours a day, the risk for employers, especially those with sedentary jobs, is quite high and very real. Employers have turned to wearable devices and other technologies as part of employee wellness programs to mitigate the risks of sitting, but very limited research has been conducted on wearable devices and their ability to reduce sitting (most wearable device studies focus on increasing physical activity). Fortunately, a study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research sought to fully understand how wearable devices can be used to reduce sitting time.
Researchers used focus groups of 15 participants to discuss sedentary behavior capabilities for 7 different wearable devices. Participants were knowledgeable about the challenges of reducing sitting time because of their prior experience in a pilot intervention targeting sedentary behavior over a three-week period. During the focus groups, participants commented on the wearability, functionality, and feedback mechanism of each device and then identified their two favorite and two least favorite devices. Participants also were asked to design and describe their ideal wearable device. The researchers took the responses and coded and analyzed the data with a thematic analysis approach.
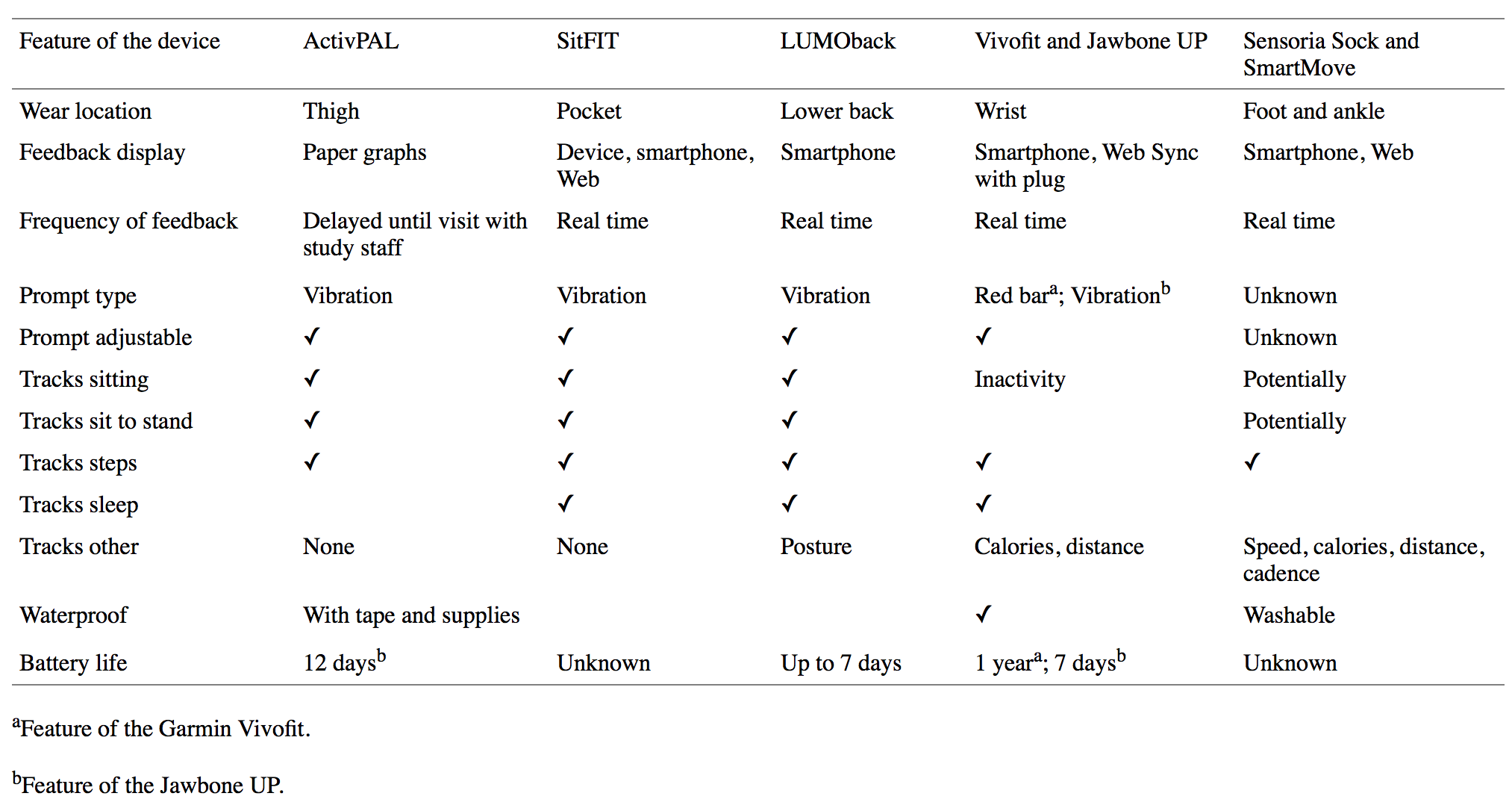
The bad news is that the study found that “current wearable devices for increasing physical activity are insufficient to intervene on sitting time.” Several participants felt that the device options were so insufficient that they had to use a “process of elimination” rather choosing favorites because none of the devices were ideal for reducing sitting time. The good news is that participants identified features that wearable devices need to reduce their sitting, including being waterproof, longer battery life, accuracy in measuring sitting time, real-time feedback on progress toward sitting reduction goals, and flexible options for prompts to take breaks from sitting.
 Most wearable devices and other digital wellness technologies, especially those used in employee wellness programs, are more focused on increasing physical activity and improving nutrition and do not have dedicated monitoring and feedback tools to reduce sitting. It is important to note that the study was conducted in late 2014 (although the findings are just being released now), and since this time, many of the requested features have been delivered by some or many of the new devices in the market. However, Apple Watch is the only major device with an emphasis on time spent sitting. With Apple Watches being cost prohibitive for most employers, wearable device companies like Garmin and Fitbit should be able to gain additional market share in employee wellness programs by offering and marketing sitting reduction features.
Most wearable devices and other digital wellness technologies, especially those used in employee wellness programs, are more focused on increasing physical activity and improving nutrition and do not have dedicated monitoring and feedback tools to reduce sitting. It is important to note that the study was conducted in late 2014 (although the findings are just being released now), and since this time, many of the requested features have been delivered by some or many of the new devices in the market. However, Apple Watch is the only major device with an emphasis on time spent sitting. With Apple Watches being cost prohibitive for most employers, wearable device companies like Garmin and Fitbit should be able to gain additional market share in employee wellness programs by offering and marketing sitting reduction features.












